Audio compression, sometimes referred to as digital audio compression, is a form of signal processing that removes unwanted audio signals. One of the most common types of audio compression is called “lossless compression.” In lossless compression, the desired audio file is transformed into a constant signal that is compressed into a lower signal that still has the selected dynamic range. Digital audio compression is used in speech applications, game development and telecommunication applications, and compression for Internet audio streaming. This article looks to answer that common question – how do I clean up bad audio? – and explain the basics.
Why is Audio Compression Necessary
Why is digital audio compression necessary? The use of audio compression in today’s computer world is more than just an annoyance. Audio compression can help reduce the bandwidth used by audio software while enhancing compressed files’ audio quality. A lossless audio compression is a helpful tool for creating web pages with sounds but does not require streaming. Audio compression is also used in some games. If a game’s audio is compressed, the player does not have to wait for buffering on the audio input device.
Lossless vs. Lossy Compression
What is the difference between lossless audio compression and lossy compression? Lossless compression compresses data without changing the original file. It is typically used to extract individual data blocks from more extensive data sets. LZ-compression (also known as low-level data compression) and MP3 compression use stages of compression that remove data that are already present in the original data stream. A typical lossless audio compression process starts by compressing all data needed, then replacing all data that is not required with filler data, which is a small, pre-compressed block of the original data.
LZ Compression
Why is LZ compression significant? Since LZ compression takes away the information that is not needed, the compressed audio will be less likely to generate false alarms. An ideal audio compressor should compress the audio without disturbing the data that is currently present.
What is the difference between conventional audio compression and true audio compression? True audio compression uses one fixed combination of stages. The typical compression method, which is referred to as true audio compression, uses four stages:
4 Factors for Audio Compressors
There are several factors to consider when determining the best audio compressor. One factor is the bit depth, which is the quality of the compression of the bit rate of the file. Another factor is the sample size, which is the total number of samples taken during playback. The third factor is the buffer size, which is the space used for audio compression. The fourth and final factor is bandwidth, which is the rate at which the compressor can process audio data.
How Does a Compressor Work
How does the compressor work? During playback, the audio is split into blocks. Each block is converted to its respective sample rate. The audio data is then compressed into a compressed file, which has a smaller file size.
How to Compress Audio
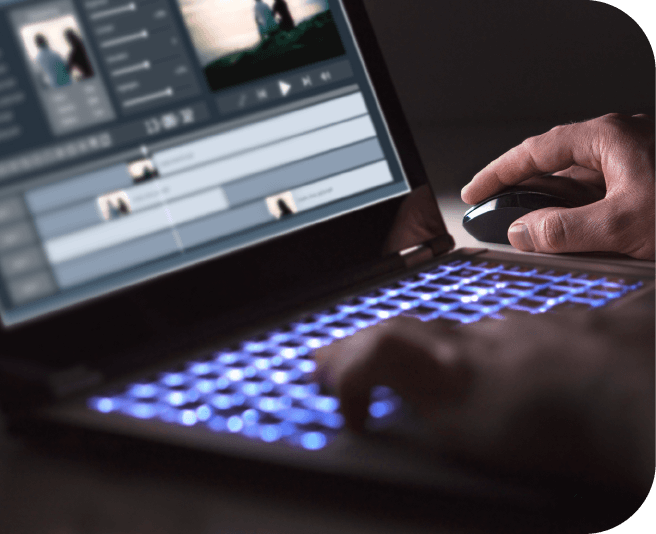
How do I compress audio? Most audio editors have the capability to compress audio and video files. Using the audio tools in your audio editing program, you can compress your audio file. The audio compression option that is available from your audio editing software is called “native.” It is recommended to use the built-in format instead of using MP3 or WAV files during audio editing because there is usually a limit on the size of compressed file that is allowed.
What effect does the audio compression have on my file size? The file size of the compressed file will be reduced by approximately 32%. Some audio compressor compressors compress the audio data without losing the quality of the audio.
Quality of Compressed Audio
How is the quality of the compressed audio file affected? The compressed audio file usually sounds better than the non-compressed audio file. Some compressors are capable of limiting the bit rate of the compressed audio file. This feature can ensure that the file quality does not get compromised, and is a great option when it comes to audio for podcasts.
Compressors and Software
What do I need to do if I want to compress audio? One thing that you should do is to find an appropriate compressor. You can look for reviews and compare various compressors. Another thing that you need to do is to use high-quality audio software in compressing audio. Then, you can make sure that the audio file is converted to its compressed form as the compressed file will have better quality.