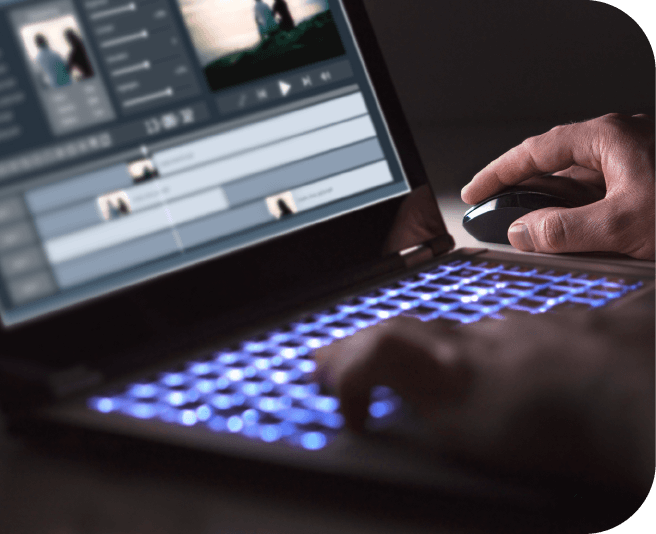
Video frame averaging is one of the most important concepts involved in statistical film analysis. Frame averaging consists in calculating the difference between two randomly selected frames and comparing it to the average of all the frames. The concept is handy in analyzing any motion picture, but particularly in movies and videos.
Frame Averaging
Video frame averaging can be used to investigate any number of factors, including camera movement, camera angles, filming time, aperture settings, shooting distances, and frame rates. For every frame, the difference between it and the average will tell you about the film’s general state. If the difference between frames is more significant than zero, it is said to have a blurring effect on the picture. This is because different parts of the frame are getting hit at different times, and because of that, parts of the frame get blurred until they no longer make any sense. This blurring is referred to as the ‘fuzz.’
For instance, if you take the average of four different frames, you can use it to determine the intensity on the average. You can then calculate how far each point on the average histogram lies from the standard. This will tell you how much of the image gets away from the center of the frame and how much is in the top left corner or right corner of the frame.
Average Histograms
One can use frame averages to find out about the focal points or critical events in the scene. Average histograms will show you the focal areas of the picture. You can then calculate how much better or worse the focal points are when compared to the other regions of the frame. To do this, you must first divide the frame into equal thirds. Then, determine which average position has the best focal event for your image.
There are many types of average histograms. For instance, the dot histogram compares the sum of all the elements in an image. The logarithm sums the values and divides them by the number of values. Finally, the cumulative average histogram sums all the values of an image over time. These three types of average histograms help find out how well a picture is composed.
Cubic Average
A cubic average histogram gives you the value of the average intensity across the whole frame. It is similar to the algorithm, but this type calculates squares’ sums rather than the numbers. The range can be plotted on a circle or some other figure, so you can plot it on a graph or scatter the points more naturally. With the cubic average histogram, you can plot a line through the points for a clearer idea of where the peak lies. You can determine the average focal point of a scene.
A candlestick histogram compares the color of each box with the color of the rest of the boxes. The same goes for a bar chart, but instead of giving you the range over time, you can plot the color distributions over a shorter range of time frames. You can also average these histograms to get a color-quality average instead of the average intensity. The bar and candlestick histograms are also helpful in judging the average color saturation or levels.
Conclusion
There are many uses for what is video frame averaging. Whether you are a filmmaker with an editor, a graphic designer, or a customer, knowing your colors’ average values can help you decide what colors will look best for your project. Histograms can also be used to make final visual decisions about the video frame for your projects, such as the color balance and the main highlights or threats your audience needs to see. Knowing the average of these colors can help you choose a successful video for your audience.